The human body has an extraordinary ability to heal itself, working through a series of biological processes to repair tissues, restore function, and maintain overall health. Whether recovering from an injury, surgery, or physical exertion, the body’s healing mechanisms follow a structured process influenced by multiple factors.
Understanding these natural mechanisms allows individuals to optimize recovery and reduce downtime by adopting habits that support healing efficiency.
Recovery time varies based on the severity of the condition, overall health status, and external factors such as nutrition, sleep, and circulation.
By exploring the body’s intricate repair systems, we can better understand what promotes faster healing and how to maximize the body’s innate regenerative abilities.
The Body’s Healing Mechanisms: How Different Hormonal Signals Affect Healing
The body’s ability to heal relies on various biological signals that regulate inflammation, tissue repair, and overall recovery efficiency. Among these, hormonal signals play a crucial role in coordinating cellular responses to injury or exertion.
Different hormonal pathways influence the speed and effectiveness of healing, with some mechanisms promoting steady, controlled recovery while others trigger more intense but fluctuating responses.
Some recovery mechanisms prioritize gradual, sustained healing by regulating inflammation and cellular regeneration over time, while others stimulate a more immediate but variable response. The balance between these processes determines how efficiently the body repairs itself.
For instance, Ipamorelin vs GHRP 6 discussions often highlight how these two compounds influence recovery in distinct ways—one promoting a steady, controlled release of biological signals, while the other triggers a more aggressive but less regulated response. Understanding these differences underscores the importance of hormonal balance in optimizing the body’s natural healing processes.
The Cellular Basis of Healing and Regeneration
At the core of the body’s healing mechanisms is cellular repair and regeneration. Cells are responsible for replacing damaged tissues, ensuring proper function is restored after an injury. The efficiency of this process varies based on tissue type:
- Epithelial tissues (such as skin and internal organ linings) regenerate rapidly due to their high cell turnover rate.
- Muscle tissues undergo repair through satellite cells that reinforce damaged fibers or replace them with scar tissue.
- Connective tissues (like tendons and ligaments) heal slowly due to limited blood supply, making recovery more prolonged.
- Nervous tissues have limited regenerative capacity, particularly in the central nervous system, though peripheral nerves can recover under certain conditions.
The body orchestrates this process by sending chemical signals that direct cells to the affected area, ensuring efficient healing. Understanding cellular regeneration helps in adopting practices that support tissue repair and minimize recovery time.
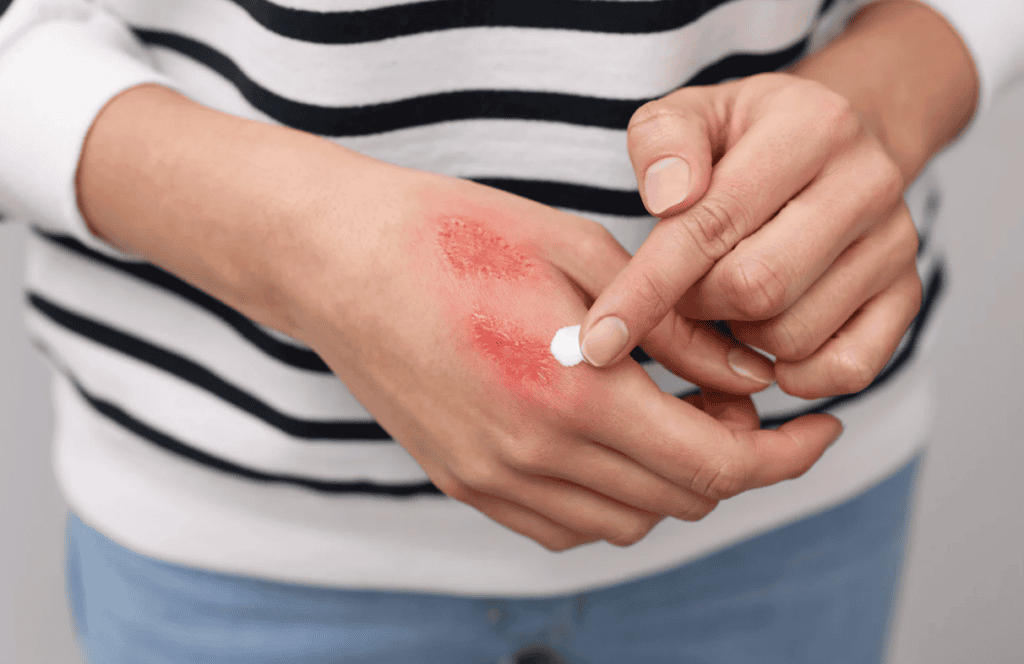
The Role of Inflammation in Recovery
Inflammation is a crucial phase of healing that serves to eliminate harmful agents, remove dead cells, and initiate repair. This biological response unfolds in several stages:
- Inflammatory Initiation – The immune system detects damage and releases chemical signals to attract white blood cells.
- Cellular Cleanup – Macrophages and other immune cells remove debris and harmful substances, paving the way for tissue regeneration.
- Inflammatory Resolution – The body reduces inflammation to prevent excessive tissue damage and promote healing.
- Tissue Remodeling – New tissue is formed, restoring strength and function to the affected area.
While inflammation is essential for recovery, prolonged or excessive inflammation can slow down healing and cause complications. Managing inflammation through proper nutrition, hydration, and rest ensures a balanced and effective recovery process.
Key Factors That Influence Recovery Speed
The speed and effectiveness of healing are influenced by multiple factors, including:
- Age – Younger individuals generally experience faster healing due to higher cellular regeneration rates.
- Nutrition – A balanced diet provides the necessary nutrients for tissue repair.
- Hydration – Proper hydration aids in cellular function and toxin removal.
- Sleep Quality – Deep sleep promotes hormonal release, which is essential for tissue recovery.
- Activity Levels – Moderate movement improves circulation, but excessive strain can delay healing.
- Medical Conditions – Chronic illnesses, such as diabetes and autoimmune disorders, can impair the healing process.
By addressing these factors, individuals can create an environment that optimizes recovery and minimizes downtime.
The Importance of Circulation in Healing
Efficient circulation is essential for delivering oxygen and nutrients to damaged tissues, ensuring faster recovery. The cardiovascular system plays a crucial role in healing by supplying blood to injured areas. Several strategies help maintain optimal circulation:
- Gentle Movement – Light exercise promotes blood flow without straining recovering tissues.
- Massage Therapy – Helps reduce stiffness and improve circulation to affected areas.
- Hydrotherapy – Alternating between hot and cold water can stimulate blood flow and reduce swelling.
- Controlled Breathing Techniques – Deep breathing enhances oxygen distribution throughout the body.
By supporting circulation, individuals can enhance their recovery process and prevent complications related to poor blood flow.
The Role of Sleep in Accelerating Recovery
Sleep is one of the most important yet overlooked factors in recovery. During deep sleep, the body undergoes critical repair processes, including:
- Increased hormone production that aids in tissue regeneration.
- Strengthened immune function, which helps combat infections and inflammation.
- Improved cognitive recovery, reducing stress and enhancing focus.
- Enhanced muscle relaxation, minimizing tension and stiffness.
To maximize the benefits of sleep, individuals should establish a consistent sleep schedule, minimize screen exposure before bedtime, and create a restful sleep environment. Prioritizing sleep ensures that the body has the necessary time and resources to recover efficiently.
Nutritional Strategies for Supporting Healing
Nutrition plays a fundamental role in the body’s ability to heal. The right combination of macronutrients and micronutrients ensures that tissues have the necessary components for repair. Key dietary elements that support healing include:
- Protein – Essential for muscle and tissue repair, found in lean meats, fish, eggs, and legumes.
- Healthy Fats – Omega-3 fatty acids in fish and nuts help regulate inflammation and support cell membrane health.
- Vitamins and Minerals – Vitamin C supports collagen production, while zinc enhances immune function and cell repair.
- Antioxidants – Found in fruits and vegetables, antioxidants help combat oxidative stress, which can delay healing.
By maintaining a well-balanced diet, individuals can significantly improve their recovery efficiency.
Mental and Emotional Well-being During Recovery
Physical healing is closely connected to mental and emotional well-being. Stress and negative emotions can slow recovery by increasing inflammation and impairing immune function. Several strategies can help maintain mental resilience during recovery:
- Mindfulness Practices – Meditation and deep breathing exercises reduce stress levels.
- Social Support – Engaging with friends and family fosters emotional stability.
- Cognitive Engagement – Activities such as reading, puzzles, and creative hobbies provide mental stimulation and distract from discomfort.
Taking a holistic approach to recovery by addressing both physical and mental health ensures a more effective healing process.
All in all, the body’s healing mechanisms are intricate, involving cellular repair, inflammation regulation, circulation support, and hormonal balance. Recovery speed depends on various factors, including age, nutrition, sleep, and emotional well-being.
By adopting lifestyle habits that promote efficient healing, individuals can optimize their recovery and reduce downtime. Understanding these processes empowers individuals to take proactive steps in maintaining long-term health and resilience.


