Understanding NLP Master Practitioner Training: Dive into the world of NLP and discover the power of transformation. This training goes beyond the basics, teaching advanced techniques that will take your skills to the next level. Learn to master the tools and techniques of NLP for personal growth, career advancement, or professional coaching. With the guidance of experienced facilitators and practical exercises, you’ll gain hands-on experience and be well-prepared to create positive change in yourself and others. Get ready to unleash your full potential with NLP Master Practitioner Training!
Introduction to NLP and its benefits
Neuro-Linguistic Programming (NLP) is a powerful tool that can transform your life. By understanding how language and thought patterns influence behavior, NLP enables you to reprogram your mind and achieve personal growth. With NLP, you can improve communication skills, overcome limiting beliefs, and enhance relationships. Unlock the power of your mind and unleash your full potential with NLP training!
Overview of NLP Master Practitioner training in small groups
The NLP Master Practitioner training in small groups offers a unique and intimate learning environment. With limited participants, individuals receive personalized attention and support from facilitators. The training covers in-depth modules on NLP techniques, TIME Techniques, Master Hypnosis, and Success Coaching. Participants benefit from practical exercises, hands-on experience, and real-life application. Upon completion, individuals receive certifications as NLP Master Practitioners, equipped with the skills to transform lives.
Importance of Small Group Learning Environment
A small group learning environment in NLP Master Practitioner training offers several benefits. It allows for personalized attention and support from facilitators, creating a more intimate and engaging learning experience. Participants can actively participate in discussions, ask questions, and receive immediate feedback. The small group setting also fosters collaboration, allowing individuals to learn from each other and share insights and experiences. Overall, the importance of a small group learning environment cannot be overstated in the journey of becoming an NLP Master Practitioner.
Advantages of learning NLP in small groups
What is NLP? NLP for small groups offers numerous advantages. Participants receive personalized attention and support, fostering a more intimate and engaging learning experience. They can actively participate in discussions, ask questions, and receive immediate feedback. The small group setting promotes collaboration, allowing individuals to learn from each other’s insights and experiences. Overall, it creates a warm and supportive environment that enhances the learning journey of becoming an NLP Master Practitioner.
Facilitators’ role in enhancing the learning experience
Facilitators play a crucial role in enhancing the learning experience of NLP Master Practitioner training in small groups. They create a supportive and inclusive environment, encouraging active participation and fostering collaborative discussions. With their expertise and guidance, facilitators provide personalized attention, valuable insights, and practical tools to help participants effectively apply NLP techniques in their personal and professional lives. Their passion for NLP and dedication to the growth of each individual greatly contributes to the overall transformational journey.

Curriculum and Modules Covered
The NLP Master Practitioner training dives deep into a comprehensive curriculum, covering a wide range of modules. Participants will gain in-depth knowledge and skills in concepts such as Quantum Linguistics, Personal Values Break-through sessions, Meta Programs, Modeling, Systems Thinking, and more. Each module is designed to provide practical tools and techniques for personal and professional growth. Embark on this transformative journey and unlock your full potential with NLP Master Practitioner training.
In-depth breakdown of NLP Master Practitioner curriculum
The NLP Master Practitioner curriculum provides a deep dive into various modules, including Quantum Linguistics, Personal Values Break-through sessions, Meta Programs, Modeling, Systems Thinking, and more. Each module equips participants with practical tools and techniques for personal and professional growth. This comprehensive training enables individuals to master NLP concepts and patterns, enhancing their skills as NLP practitioners.
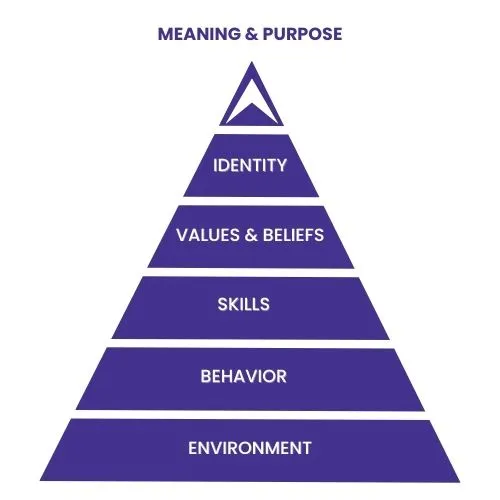
Key modules and skills taught during the training
During the NLP Master Practitioner training, participants receive comprehensive instruction in key modules such as Quantum Linguistics, Personal Values Break-through sessions, Meta Programs, Modeling, Systems Thinking, and more. This immersive experience equips individuals with practical tools and techniques for personal and professional growth, allowing them to become proficient in applying NLP concepts and patterns to transform their lives and the lives of others.
Practical Application and Hands-On Experience
Practical Application and Hands-On Experience: Unleashing the Power of NLP
In the world of NLP, theory is just the beginning. To truly master NLP, one must dive into practical application and hands-on experience. This is where the magic happens! Through interactive exercises, role-playing, and real-life scenarios, participants get to put their newly acquired NLP skills into action. From improving communication dynamics to overcoming limiting beliefs, these practical experiences allow individuals to witness the transformative power of NLP firsthand. So get ready to roll up your sleeves and embark on an exciting journey of self-discovery and growth!
Role of practical exercises in NLP Master Practitioner training
The role of practical exercises in NLP Master Practitioner training is crucial for a well-rounded learning experience. By engaging in hands-on activities, participants get to apply NLP techniques in real-life scenarios. This allows them to fine-tune their skills, gain confidence, and witness the powerful impact of NLP firsthand. From improving communication dynamics to overcoming limiting beliefs, these practical exercises are the catalysts for transformation and growth.
Opportunities for hands-on practice and real-life application
Participants in NLP Master Practitioner training have ample opportunities for hands-on practice and real-life application. Through interactive exercises and role-playing scenarios, they get to apply NLP techniques in a safe and supportive environment. These practical experiences serve as invaluable learning tools, allowing participants to see the immediate impact of NLP on communication, mindset, and personal growth. By practicing in real-world situations, individuals gain the confidence and skills to apply NLP in their everyday lives, making a tangible difference.
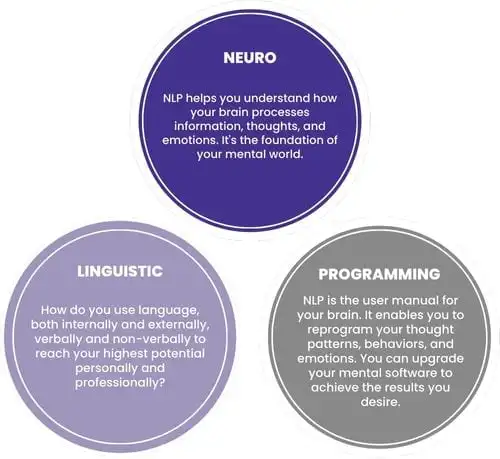
Certification and Professional Development
Once participants complete the NLP Master Practitioner training, they have the opportunity to become certified as an NLP Master Practitioner. This certification demonstrates their advanced skills and knowledge in NLP techniques and sets them apart in the professional field. Additionally, becoming a certified NLP Master Practitioner opens the door to various professional development opportunities, including advanced coaching programs and specialized workshops. It’s a rewarding journey that empowers individuals to reach new heights in their personal and professional lives.
Process of certification as an NLP Master Practitioner
Once participants complete the NLP Master Practitioner training, they have the opportunity to become certified as an NLP Master Practitioner. This certification is earned by demonstrating advanced skills and knowledge in NLP techniques. It involves a thorough evaluation of the participant’s understanding and application of NLP principles. Upon successful completion, participants receive a recognized certification that showcases their expertise and sets them apart in the field of NLP. Carving the path to success has never been easier!
Benefits of becoming a certified NLP Master Practitioner
Becoming a certified NLP Master Practitioner brings numerous benefits. It empowers individuals to enhance their communication skills, exert influence with finesse, and create positive changes in their personal and professional lives. With the invaluable tools and techniques learned, practitioners can transform their relationships, increase self-confidence, overcome obstacles, and achieve personal excellence. Certification as an NLP Master Practitioner opens doors to exciting opportunities for growth, success, and fulfillment. So why wait? Start your journey towards transformation today!
Testimonials and Success Stories
Testimonials and success stories serve as powerful evidence of the impact and effectiveness of NLP Master Practitioner training. Past participants have shared their transformative experiences, expressing their satisfaction with the small group learning environment, practical application exercises, and the guidance of skilled facilitators. These stories of personal growth and success inspire and motivate aspiring practitioners to embark on their own NLP journey.
Feedback from past participants in small group NLP training
Past participants of small group NLP training have praised the transformative experience and close-knit learning environment. They commend the quality of facilitators who offer personalized guidance and support throughout the training. Many have shared how the practical application exercises helped them apply NLP techniques to real-life situations, boosting their confidence and effectiveness. The success stories and testimonials from these participants serve as inspiration for aspiring NLP practitioners.
Success stories of individuals who transformed their lives through NLP practice
Through small group NLP training, many individuals have achieved remarkable transformations in their lives. John, a shy introvert, gained confidence and became a charismatic public speaker. Sarah, struggling with anxiety, learned to reframe her thoughts and now lives a life filled with peace and joy. These success stories serve as inspiration, showing the power of NLP in changing lives for the better.
As we wrap up, we invite you to feature your business on our website through the Accessily platform.
Read also: Insight Learning




