Understanding Telepsychiatry
What is Telepsychiatry?
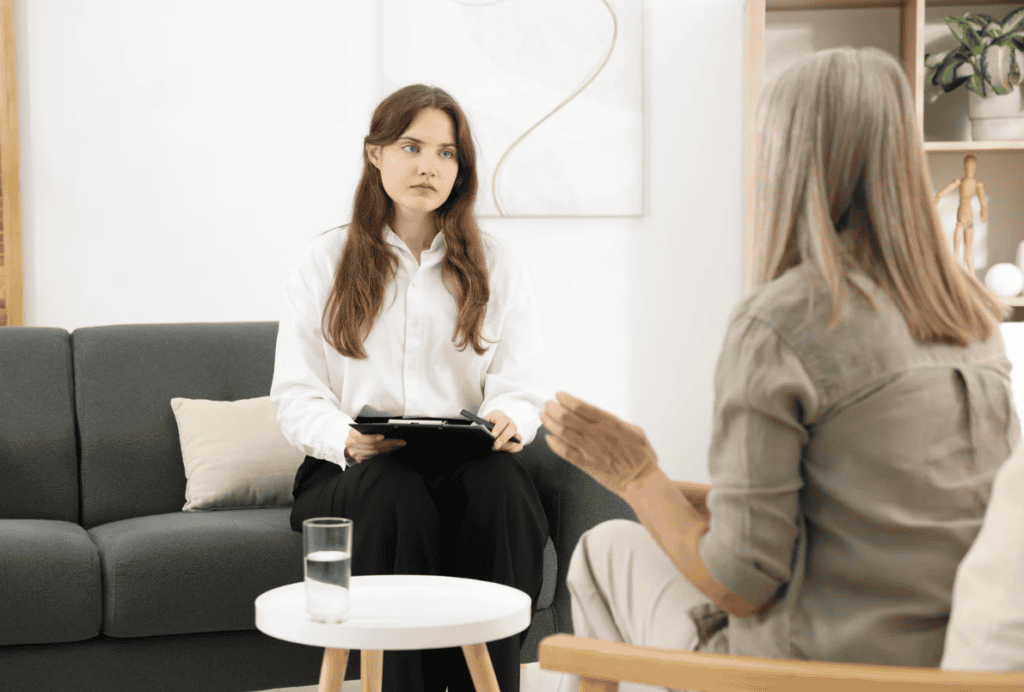
Telepsychiatry is a rapidly expanding branch of telemedicine that allows patients to receive psychiatric care remotely through digital communication technologies.
By using secure video conferencing platforms, encrypted messaging systems, and mobile health applications, individuals can connect with licensed psychiatrists without visiting a traditional clinic or hospital.
In the past, people seeking mental health treatment often had to wait weeks for appointments and travel to specialized clinics for consultations. Telepsychiatry has changed this model dramatically.
With access to a smartphone, tablet, or computer connected to the internet, patients can now receive professional psychiatric support from the comfort and privacy of their own homes.
Remote psychiatric services include a wide range of treatments such as mental health assessments, therapy sessions, medication management, follow-up consultations, and patient education.
These services are commonly delivered through real-time video sessions that allow psychiatrists and patients to interact face-to-face in a secure digital environment. In some cases, secure messaging or phone consultations are also used to provide continuous care between appointments.
Companies working in the digital health sector are playing an important role in expanding these services. FasPsych, the leading telepsychiatry company, helps connect patients with licensed psychiatrists through secure virtual platforms designed to improve access to mental health care.
Much like how online banking transformed the financial industry, telepsychiatry is transforming the way psychiatric services are delivered. By removing geographical limitations and reducing logistical barriers, remote psychiatric care makes treatment more accessible, flexible, and convenient.
For individuals dealing with anxiety, depression, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), or other mental health conditions, faster access to professional care can make a significant difference in recovery and long-term well-being.

The Evolution of Digital Mental Health Services
The concept of remote healthcare is not entirely new, but recent technological advancements have made virtual health care services far more practical and accessible. High-speed internet, cloud computing, and widespread smartphone adoption have created the infrastructure necessary for remote psychiatric care to operate efficiently.
Over the past decade, healthcare providers have increasingly adopted telehealth solutions to improve accessibility and reduce strain on traditional healthcare systems. Hospitals, private clinics, and mental health organizations now rely on digital platforms to connect patients with specialists who may be located hundreds or even thousands of miles away.
The demand for virtual healthcare services accelerated significantly in recent years as healthcare systems sought alternatives to in-person consultations. During this period, many patients experienced digital healthcare for the first time and quickly recognized its convenience.
As a result, telepsychiatry has evolved from a temporary solution into a permanent component of modern healthcare systems.
Digital mental health platforms are also becoming more advanced. Many services now integrate electronic health records, online screening tools, and mobile applications that allow patients to monitor symptoms and track emotional patterns between therapy sessions.
These technologies create a comprehensive mental health ecosystem where care extends beyond individual appointments and supports continuous mental wellness.
The Growing Demand for Mental Health Support
Global Mental Health Challenges
Mental health conditions are among the most significant public health challenges of the modern era. Disorders such as depression, anxiety, bipolar disorder, and PTSD affect hundreds of millions of people worldwide.
Growing awareness of mental health issues has encouraged more individuals to seek professional help. However, many healthcare systems struggle to meet this demand due to limited resources and a shortage of trained professionals.
In many regions, patients must wait weeks or even months before receiving psychiatric consultations. These delays can worsen symptoms and make recovery more difficult.
Virtual mental health services offers a powerful solution by enabling mental health professionals to provide care remotely. Instead of restricting services to local clinics, psychiatrists can support patients across cities, states, and even countries through secure online platforms.
This expanded reach helps bridge the gap between increasing mental health needs and limited healthcare resources.
Shortage of Mental Health Professionals
A shortage of qualified psychiatrists and therapists continues to impact mental healthcare systems worldwide. Rural communities and smaller towns often have limited access to specialized mental health services.
For many individuals living in remote areas, the nearest psychiatrist may be located several hours away. Travel expenses, scheduling difficulties, and social stigma associated with visiting mental health clinics can discourage people from seeking treatment.
Telepsychiatry helps overcome these barriers by delivering psychiatric care directly through internet-connected devices. A licensed psychiatrist can conduct consultations remotely, allowing patients to receive professional care without traveling long distances.
This model enables healthcare providers to distribute psychiatric expertise more efficiently and reach populations that previously had limited access to mental health services.
How Telepsychiatry Works
Technology Behind Telepsychiatry
Virtual mental health support relies on secure digital platforms specifically designed for healthcare communication. These systems use encrypted video conferencing technology that allows psychiatrists and patients to interact in real time while maintaining strict privacy standards.
Most platforms integrate with electronic health record (EHR) systems, allowing clinicians to review patient histories, treatment plans, and medication details during consultations. This integration ensures continuity of care even when appointments occur remotely.
Many telepsychiatry platforms also include digital assessment tools that allow patients to complete mental health questionnaires before appointments. These tools help clinicians better understand symptoms and prepare personalized treatment strategies.
Artificial intelligence is also beginning to assist telepsychiatry systems. AI tools can analyze behavioral patterns and identify changes in mood-tracking data that may indicate emerging mental health concerns.
Although these technologies do not replace human expertise, they provide additional insights that help clinicians deliver more personalized care.
Key Benefits of Telepsychiatry
Accessibility and Convenience
One of the greatest advantages of telepsychiatry is its ability to remove physical barriers to care. Patients no longer need to travel long distances, rearrange busy schedules, or wait in crowded clinics for appointments.
Instead, therapy sessions can take place from the privacy of home or another comfortable environment. This convenience improves attendance rates and helps patients maintain consistent treatment plans.
For individuals with physical disabilities, chronic illnesses, or demanding work schedules, remote consultations provide a highly practical solution.
Reduced Mental Health Stigma
Despite increased awareness, stigma surrounding mental health treatment still exists in many communities. Some individuals feel uncomfortable visiting psychiatric clinics because they worry about being judged by others.
Telepsychiatry offers a more discreet way to access professional care. Patients can attend therapy sessions privately without drawing attention to their treatment.
This privacy encourages individuals to seek help earlier, which can significantly improve long-term mental health outcomes.
Cost Efficiency
Telepsychiatry also provides economic benefits for both patients and healthcare providers. Clinics can expand their services without investing heavily in additional office space or infrastructure.
Patients save money on travel costs, parking fees, and time away from work. Remote consultations also allow psychiatrists to manage appointments more efficiently, enabling them to serve more patients each day.
These efficiencies make telepsychiatry an attractive solution for healthcare systems seeking to expand mental health services while controlling operational costs.

Telepsychiatry in Rural and Underserved Areas
Telepsychiatry has become especially valuable for rural communities where mental health specialists are scarce. Many smaller towns lack resident psychiatrists, leaving local healthcare providers without specialized mental health support.
Through telepsychiatry, rural clinics can connect with remote psychiatrists who provide consultations and treatment plans for patients in their communities.
Schools, community health centers, and primary care clinics increasingly rely on telepsychiatry systems to provide mental health support to students, families, and vulnerable populations.
Children, elderly individuals, and patients with mobility challenges particularly benefit from remote psychiatric services because traveling long distances for treatment can be physically and financially difficult.
Telepsychiatry vs Traditional Psychiatry
| Feature | Telepsychiatry | Traditional Psychiatry |
| Location | Remote consultations | In-person clinic visits |
| Accessibility | Available from anywhere | Limited by location |
| Convenience | Flexible scheduling | Fixed appointments |
| Cost | Often lower | Higher operational costs |
Research shows that telepsychiatry can deliver treatment outcomes comparable to traditional therapy for many common mental health conditions when services are provided by qualified professionals.
Challenges and Limitations
Although telepsychiatry offers many advantages, certain challenges remain. Data privacy and cybersecurity are significant concerns because mental health information is highly sensitive.
Healthcare providers must ensure telepsychiatry platforms follow strict security standards and use advanced encryption to protect patient confidentiality.
Technological barriers can also limit access for some individuals who lack reliable internet connections or experience difficulty using digital tools.
Continued investment in digital infrastructure and user-friendly healthcare platforms will be essential for overcoming these challenges.
The Future of Telepsychiatry
The future of telepsychiatry looks highly promising as healthcare systems continue adopting digital innovations. Emerging technologies such as wearable health devices, AI-supported diagnostics, and virtual therapy environments are expected to further enhance remote psychiatric care.
Governments, healthcare organizations, and technology companies are investing heavily in digital mental health platforms designed to improve accessibility and treatment outcomes.
As these technologies continue to evolve, telepsychiatry will likely become a standard part of modern healthcare systems worldwide.
Conclusion
Telepsychiatry is transforming mental healthcare by combining professional psychiatric expertise with advanced digital technology. By removing geographical barriers, reducing stigma, and improving accessibility, it enables individuals to receive mental health support more easily than ever before.
As global demand for mental health services continues to rise, telepsychiatry provides a scalable and effective solution for delivering professional psychiatric care to diverse populations.
With continued innovation and responsible integration into healthcare systems, telepsychiatry is set to play a vital role in shaping the future of mental health treatment.
FAQs
1. What conditions can telepsychiatry treat?
Telepsychiatry can treat a wide range of mental health conditions including depression, anxiety disorders, bipolar disorder, PTSD, ADHD, and sleep disorders. It is also commonly used for therapy sessions, medication management, and psychiatric evaluations.
2. Is telepsychiatry as effective as in-person therapy?
Many studies show that telepsychiatry produces outcomes comparable to traditional therapy for common mental health conditions when conducted by licensed professionals.
3. Do insurance companies cover telepsychiatry?
Yes, many insurance providers and government health programs now cover telepsychiatry services, making remote mental healthcare more accessible and affordable.
4. Is telepsychiatry safe and confidential?
Telepsychiatry platforms typically use encrypted communication systems and secure medical software to protect patient data and ensure privacy during consultations.
5. Who benefits the most from telepsychiatry?
People living in rural areas, individuals with mobility challenges, busy professionals, and those seeking discreet mental health support benefit significantly from telepsychiatry services.