Mental health conversations are no longer happening only in clinical offices. You hear them at work, in schools, within families, and across communities. Stress, anxiety, trauma, and burnout have become part of everyday life for many people, shaped by social pressures, economic uncertainty, and rapid change. As awareness grows, so does the understanding that mental health care cannot rely on one approach alone.
Therapy and medical treatment are important, but they are not always enough. Mental health is deeply connected to a person’s environment, relationships, access to resources, and sense of stability. This is where social work plays a critical role. Social workers look at the whole picture, not just symptoms. They help people navigate systems, overcome barriers, and find support that fits their real-life situations.
In today’s mental health landscape, the need for professionals who can bridge care, advocacy, and community support has never been greater. This type of work has stepped into that space, becoming an essential part of how mental wellness is understood and supported.
How Advanced Social Work Education Supports Mental Health Care
Mental health challenges rarely exist in isolation. Family dynamics, housing stability, income, education, and access to care influence a person’s emotional well-being. This type of education is designed to prepare professionals to understand and respond to these interconnected factors in a meaningful way.
Advanced training helps social workers develop skills in assessment, counseling, case management, and ethical decision-making. It also emphasizes cultural awareness, empathy, and evidence-based practice.
If you’re interested in working directly with individuals and communities while addressing both emotional and practical needs, pursuing a Masters of Social Work program can provide the foundation needed to support mental health in diverse settings, from clinical environments to community-based organizations.
This level of education prepares them to respond thoughtfully to complex situations, offering care that is grounded, flexible, and deeply human.
The Expanding Role of Social Workers in Mental Health Services
Social workers are present across a wide range of mental health settings. You’ll find them in hospitals, schools, outpatient clinics, community centers, and nonprofit organizations. Their role often involves connecting people to services, supporting treatment plans, and advocating for ongoing care.
Unlike roles that focus on one aspect of mental health, social workers often coordinate multiple forms of support. They may help someone access counseling, secure housing, apply for benefits, or navigate healthcare systems. This flexibility allows them to meet people where they are and adjust support as needs change.
As mental health services expand beyond traditional models, social workers continue to adapt, making care more accessible and responsive.
Addressing Barriers to Mental Health Care
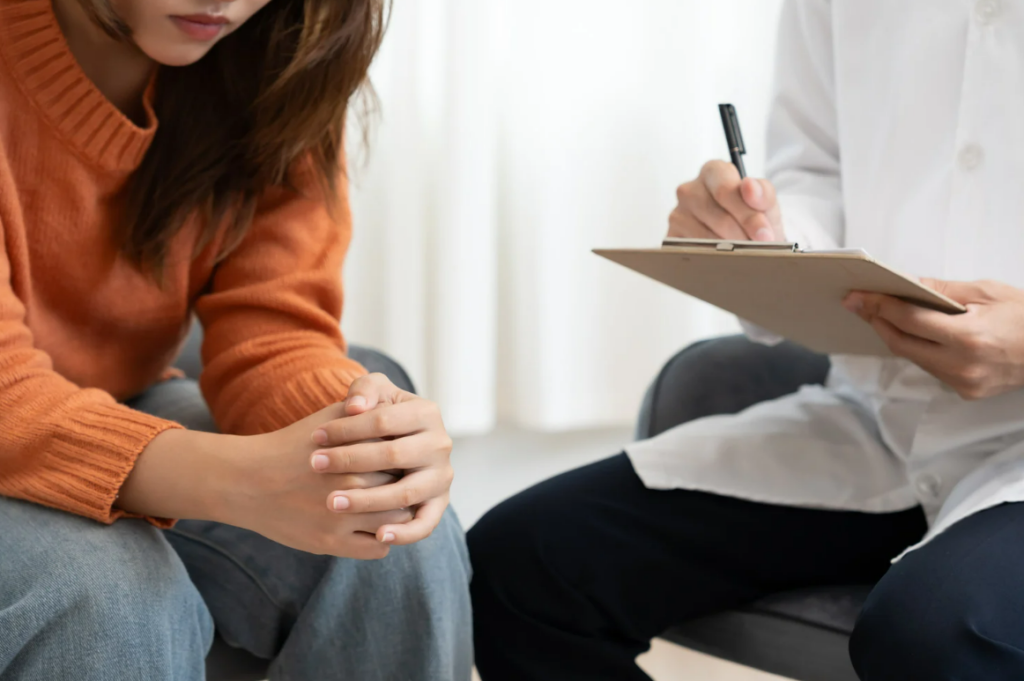
One of the biggest challenges in mental health care is access. Many people face obstacles such as cost, transportation, stigma, or lack of information. Even when services exist, navigating complex systems can feel overwhelming, especially during times of crisis.
Social workers play a key role in reducing these barriers. They help individuals understand their options, connect with resources, and move through systems that might otherwise feel impossible to manage alone. This advocacy ensures that mental health support is not limited to those who already know how to access it.
By focusing on equity and access, this helps bring mental health care to people who might otherwise fall through the cracks.
Social Work’s Holistic Approach to Mental Wellness
Mental wellness is not just about treating symptoms. It’s about creating conditions where people can feel stable, supported, and hopeful. Social work takes a holistic approach, considering social, economic, and environmental factors alongside emotional health.
This perspective recognizes that stress from housing insecurity, financial strain, or family conflict can deeply affect mental well-being. Social workers address these issues directly, helping individuals build stronger foundations for recovery and resilience.
By looking beyond immediate concerns, social work supports long-term mental wellness rather than short-term relief.
Supporting Individuals and Families Through Crisis and Change
Life transitions and crises can place immense strain on mental health. Events such as loss, illness, displacement, or sudden change often leave people feeling overwhelmed and unsure where to turn. Social workers are trained to provide steady support during these moments.
They help individuals and families process what’s happening, make informed decisions, and find stability during uncertainty. This support is not rushed or transactional. It’s built on trust, compassion, and consistent presence.
Through crisis intervention and ongoing guidance, social workers help people regain a sense of control and move forward with confidence.
The Connection Between Social Work and Community Mental Health
Mental health does not exist only at the individual level. Communities play a powerful role in shaping well-being. Social workers often work at the community level, supporting programs that promote education, prevention, and collective resilience.
Community-based mental health efforts may include outreach, support groups, and partnerships with local organizations. Workers help design and implement these initiatives, ensuring they reflect the real needs of the people they serve.
By strengthening communities, they contribute to mental health outcomes that extend far beyond individual treatment.

Collaboration Between Social Workers and Mental Health Professionals
Effective mental health care often depends on teamwork. Social workers regularly collaborate with psychologists, counselors, doctors, educators, and other professionals. This collaboration helps ensure that care is coordinated and comprehensive.
Social workers often act as connectors, sharing information and aligning services so individuals don’t feel lost between providers. Their ability to communicate across disciplines improves continuity of care and reduces gaps in support.
This team-based approach reflects the reality that mental health care works best when professionals learn from one another and work toward shared goals.
Preparing Social Workers for Ethical and Emotional Challenges
Working in mental health can be emotionally demanding. Social workers face ethical dilemmas, complex client situations, and the emotional weight of supporting others through hardship. Education prepares them not only with technical skills but also with tools for self-awareness and resilience.
Training emphasizes ethical responsibility, boundaries, and reflective practice. This preparation helps social workers remain grounded and effective while protecting their own well-being. By learning how to navigate challenges thoughtfully, social workers are better equipped to provide consistent and compassionate care.
Why Social Work Will Continue to Matter in the Future
Mental health needs are not expected to decrease anytime soon. As societies continue to face social change, inequality, and new stressors, the role of social work will remain vital. The profession’s adaptability allows it to respond to emerging challenges and evolving care models.
This type of education prepares professionals to grow alongside these changes, ensuring that mental health support remains relevant and accessible. Its emphasis on human connection, advocacy, and holistic care makes it uniquely suited to meet future demands.
It has become essential in today’s mental health landscape because it addresses what people truly need: care that recognizes the full complexity of their lives. By combining emotional support with practical assistance, advocacy, and community engagement, social workers help bridge gaps that other approaches cannot fill.
As mental health awareness continues to grow, social work stands as a cornerstone of meaningful, compassionate care. Its impact reaches individuals, families, and entire communities, making it an indispensable part of how mental wellness is supported now and into the future.