Purpose of Drug Testing in Modern Workplaces
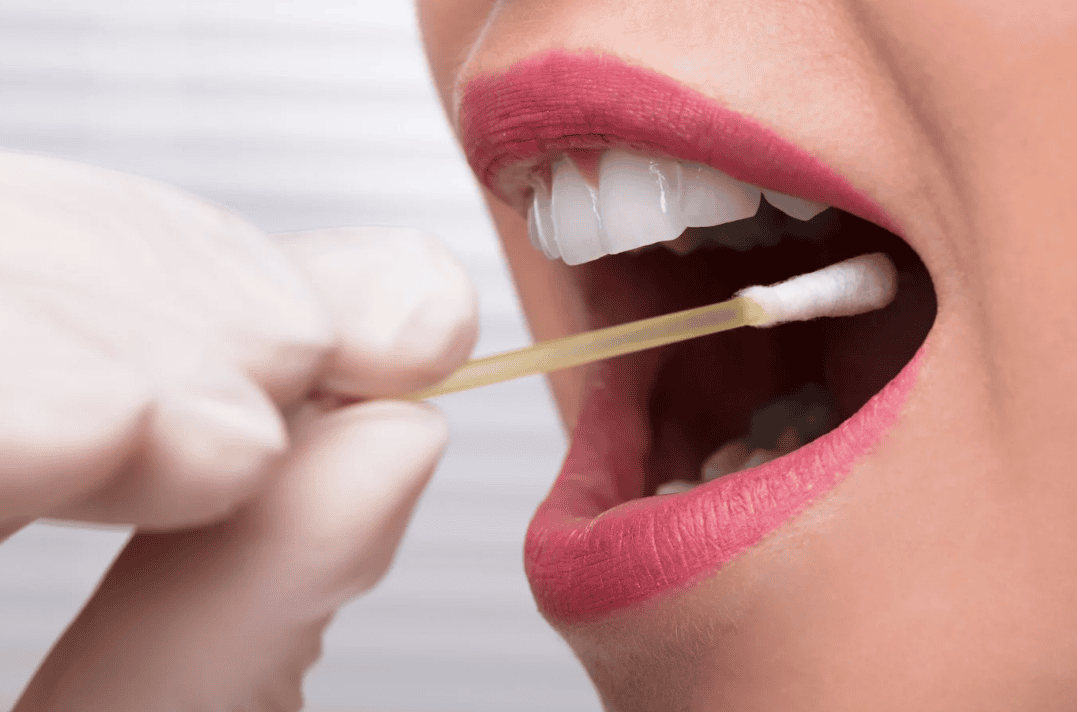
Drug testing is employed in modern workplaces to maintain safety and productivity of workers. It assists the employers to detect and manage substance addictions, minimise accidents, and adhere to the industry regulations. Saliva testing is gaining widespread use because it is simple, non-invasive, and quick and reliable.
The benefit of saliva drug test kits for employers is that they can be tested on site with little preparation and guarantees fast decision making and workplace integrity. Recent drug use is also identified in this method and this makes it popular among employers who are concerned with their employees safety.
Employers can choose a wide variety of drug testing methods, all of which have advantages and disadvantages based on the requirements of the company. Common are urine, hair follicle, blood and saliva tests. Urine testing is well favored because of its large detection window and long detection window. Hair follicle test indicates the chronic patterns of substance use whereas blood test is precise yet invasive.
Nonetheless, saliva drug test kit near me is non-invasive and rapid and convenient, enabling it to be a flexible choice of workplace screening. Saliva drug test kits for employers can be used in jobs with safety sensitivities and which demand rapid outcomes as it can reveal the recent use of drugs. Its simplicity and trustworthiness, make it an essential device in the contemporary screening of employment.
How Saliva Drug Tests Work
Saliva drug test kits are non-invasive and simple to use in the detection of saliva drugs. These kits are important in ensuring safe and productive working environments by allowing companies to screen drugs fast and accurately. Saliva drug test kits for employers test a short sample of saliva to analyze marijuana, cocaine, amphetamines and opioids. The method usually provides solutions within a few minutes, and companies can make decisions regarding safety and compliance in a few minutes.
Oral fluid tests are found in marijuana, cocaine, amphetamines, methamphetamines, painkillers and performance-impairing medicines. They are applicable in safety-oriented companies such as construction, transportation and manufacturing where lack of sense may be hazardous.
This has led to employment drug test kits of saliva being used to conduct pre-employment screening, random drug tests, and post-incident investigations in an attempt to maintain a drug-free workplace. Their accuracy and capability to diagnose recent use of substances assist in maintaining the compliance and safety.
Benefits of Using Saliva Drug Tests
Numerous of saliva drug test kits for employers not only provide credible results within minutes, but they enable companies to make timely decisions without compromising business.
Testing of saliva is a non-invasive testing method, which does not need any special equipment or preparation as opposed to blood and urine tests. On-site saliva testing also reduces the workdays and loss of workforce.
The saliva test is painless, confidential, and has no special collection protocols such as blood or urine testing that are required by the specialists. The process is easy because workers can provide a sample of saliva under monitoring.
This ease facilitates the compliance and collaboration of employees and does not require expensive infrastructure or big logistics. Saliva drug test kits for employers are non-invasive, making testing easier for everyone and leading to a more productive and stress-free workplace overall.
Tampering is greatly avoided using saliva drug test kits for employers. Saliva testing is monitored lowering chances of sample replacement or adulteration. Such real-time method of collections enhances dependability of results and guarantees that testing reflects a current usage of drugs by an employee.
The saliva drug test kits minimize tampering weaknesses and employers are able to administer a better and more dependable testing initiative, which guarantees a secure and more compliant workplace.
Saliva drug tests kits are perfect in on-site and random testing, which is useful to companies. They are effective in the work place because these kits are portable and simple to work with as well as fast. It is best suited to any random testing that needs a rapid collection of samples. On-site testing is more time and resource saving since it dispels staff travel.
Legal and Compliance Considerations
Drug testing laws in the workplace help to balance between the privacy of the employees and the safety of the working environment. Employers have to comply with federal, state, and local regulations regarding drug testing and they usually involve clear consent.
Non-invasive saliva drug test kits for employers are popular due to their speed and accuracy. In order to adhere to the legal and ethical standards, companies have to carry out tests in an open manner, inform workers, and keep the results secret. Organizations can enhance safety in the workplace and guard the privacy and faith of the employees.
Industry-specific compliance standards are common in drug testing programs in other safety-critical industries such as transportation, healthcare, and manufacturing. These necessities involve comprehensive works in documentation, record keeping, and testing.
Employers should be able to access and audit the consent forms, test results and notifications to ensure their secure maintenance. Proper records indicate regulatory conformity, shield firms against lawsuits and promote ethical and legal working practices.
Types of Saliva Drug Test Kits Available
Saliva drug test kits in companies are suitable in drug testing at workplace, law enforcement, and personal purposes as they provide fast and accurate results within a few minutes.
Saliva samples are collected on a swab and tested using instant read test kits that do an analysis of the sample. They are able to identify the presence of THC, cocaine, opiates, and amphetamines and as a result, they are suitable in on-the-spot testing.
They can be applied to provide instant outcomes since they are precise and convenient to use.
Laboratory-based collection kits are suited to full and legally admissible findings. Laboratory-based saliva drug test kits for employers gather a saliva sample on-site and securely send it to a certified facility for examination. This method is able to identify a broad spectrum of different chemicals providing reliable results.
The cost-effective and efficient multi-panel saliva drug test kits for employers screen a wide spectrum of drugs in one test. Nonetheless, a single-drug test kits are designed to detect a single drug and hence to be used in instances of known drug issues. The two techniques are both accurate though multi-panel kits are preferable in general testing and single-drug kits in individual research.

Key Features Employers Should Evaluate
Ease of Use for Administrators
Administrator ease of use is important while choosing saliva drug test kits for employers. A basic kit will minimize mistakes and give valid results in the course of testing. Kits administrators have to select those with easy instructions, minimal preparation, and easy sample collection and handling tools. It can be made simple to use in order to enhance drug testing efficiency and reliability.
Clarity of Test Results
Test results must be unambiguously positive, negative, or inconclusive otherwise they can be misinterpreted. Indications are labeled such as color change or digital displays to minimize errors because these give immediate feedback.
Moreover, elaborate data interpretation instructions or manuals may be priceless. One way that employers can increase the accuracy and confidence of drug testing is by selecting kits whose test outcomes are well defined.
Shelf Life and Storage Requirements
Long shelf life ensures that test kits are effective, which saves on wastage and re-stocking. Storage requirements such as temperature and humidity should be known to provide test accuracy and reliability. Flexible storage kits or stable under varying conditions result in a more convenient and accommodating drug testing in workplaces and accommodating to business.
Quality Control Standards
The quality control standards of the manufacturer of drug test kits should be keenly examined by the employer in order to obtain the accuracy and reliability of the test kits. Good quality kits are batch tested, well labelled and certified by the FDA or ISO.
These criteria will provide the consistency of performance, minimizing false positives and negatives which would impair results credibility. Built-in quality control checks are available in kits like control lines or indicators to ensure companies keep a high level of compliance and professional standards during testing.
Choosing the Right Saliva Drug Test Kits for Employers
Companies need to take a closer look at a number of vital variables when assessing prospects to make educated recruiting decisions. Qualifications and experience in the line of duty usually denotes the capability of the candidate to meet the task.
Soft skills such as communication, flexibility, and teamwork have an impact on workplace harmony and collaborations, and therefore, they should be evaluated. Employers also have an opportunity to determine the cultural fit to determine whether the candidate shares values and ambitions of the company.
Last but not least, a proper reference check and properly designed interview may show the reliability, work ethics and potential to make the team a success of the candidate.
Saliva drug test kits for employers will be profitable by ensuring a safer and more productive work environment. To keep the test reliable and without bias, quality, and reliable testing kits should be maintained which would minimize the error and give accurate results.
Ethical conduct(choosing regulatory compliant kits) assists firms to evade legal matters and display ethical conduct. By introducing smart, properly designed testing programs, employers can enhance the well-being of their employees, the rates of substance use, and the culture of responsibility and care that will be beneficial to both the company itself and its employees.